UniC-Lift
Unified 3D Instance Segmentation via Contrastive Learning
Abstract
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have advanced novel-view synthesis. Recent methods extend multi-view 2D segmentation to 3D, enabling instance/semantic segmentation for better scene understanding. A key challenge is the inconsistency of 2D instance labels across views, leading to poor 3D predictions. Existing methods use a two-stage approach in which some rely on contrastive learning with hyperparameter-sensitive clustering, while others preprocess labels for consistency. We propose a unified framework that merges these steps, reducing training time and improving performance by introducing a learnable feature embedding for segmentation in Gaussian primitives. This embedding is then efficiently decoded into instance labels through a novel "Embedding-to-Label" process, effectively integrating the optimization. While this unified framework offers substantial benefits, we observed artifacts at the object boundaries. To address the object boundary issues, we propose hard-mining samples along these boundaries. However, directly applying hard mining to the feature embeddings proved unstable. Therefore, we apply a linear layer to the rasterized feature embeddings before calculating the triplet loss, which stabilizes training and significantly improves performance. Our method outperforms baselines qualitatively and quantitatively on the ScanNet, Replica3D, and Messy-Rooms datasets.
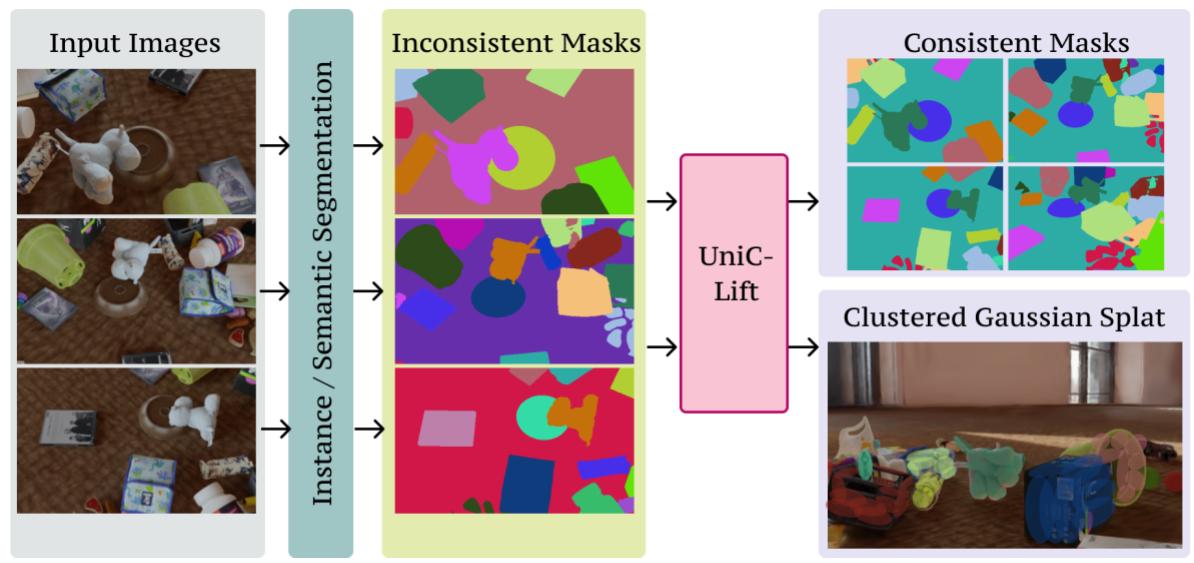
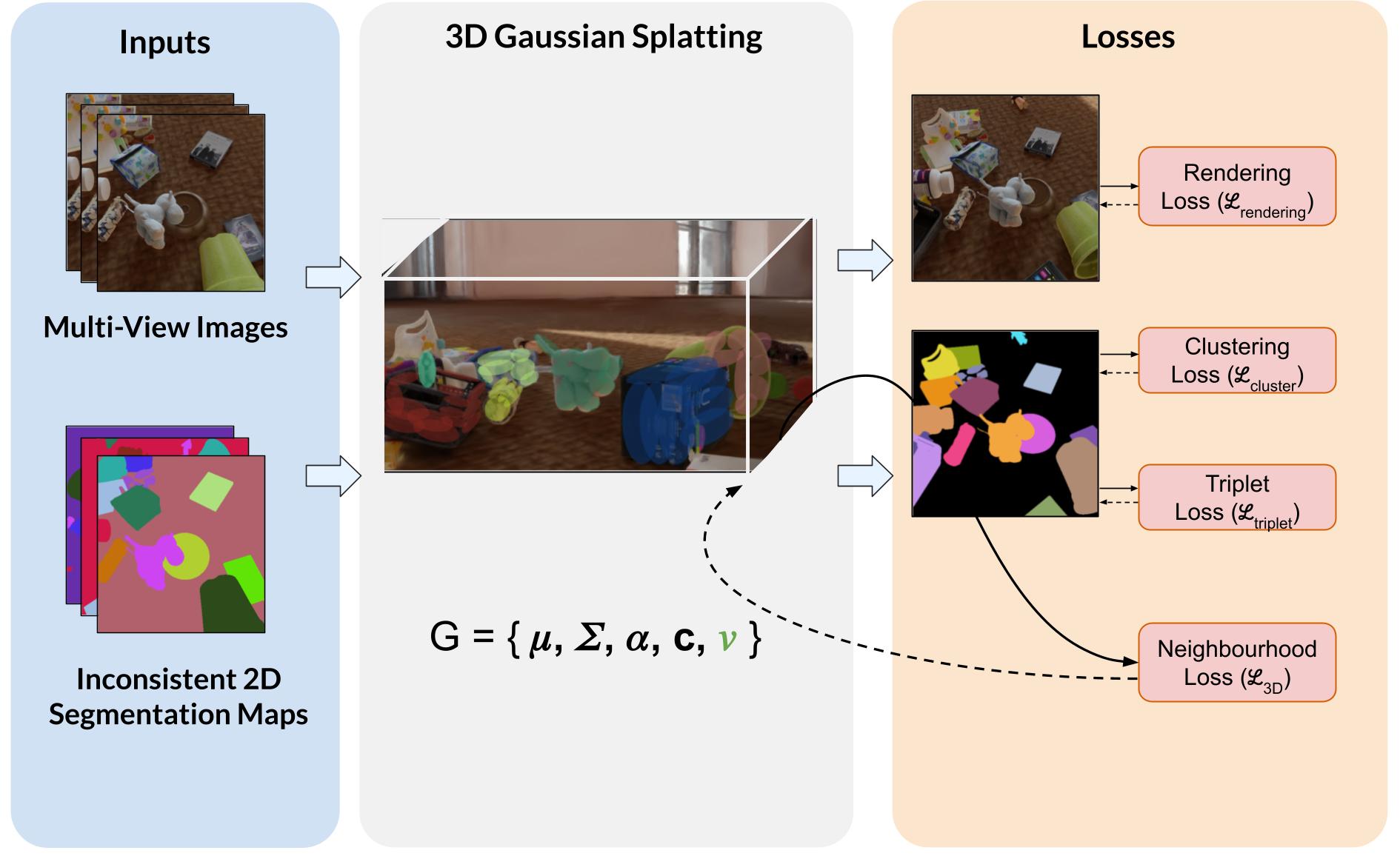
Method Overview
The model takes multi-view images and their inconsistent 2D instance segmentation maps as input. These are lifted into a 3D Gaussian Splatting representation, where each Gaussian is associated with a learnable embedding. Training is guided by the following objectives:
Rendering Loss
Ensures photometric consistency across views.
Contrastive Loss
Encourages embeddings of the same instance to group together.
Triplet Loss
Enforces margin separation between distinct instances.
Neighborhood Loss
Regularizes embeddings for spatial smoothness in 3D.
Citation
@article{dhiman2025unic,
title={UniC-Lift: Unified 3D Instance Segmentation via Contrastive Learning},
author={Dhiman, Ankit and R, Srinath and Reddy, Jaswanth and Boregowda, Lokesh R and Radhakrishnan, Venkatesh Babu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.24763},
year={2025}
}